First, the composition of the ultraviolet radiation meter
The wavelength of ultraviolet radiation is about 100 nm to 400 nm, and the instruments used to measure the illuminance of ultraviolet radiation are generally divided into four bands of ultraviolet radiation, A1, A2, B, and C. A1 band (320 ~ 390) nm, peak wavelength (360 ± 5) nm; A2 band 365 nm, peak wavelength (365 ± 1) nm; B band (290 ~ 320) nm, peak wavelength (310 ± 5) nm; C Band 253.7nm, peak wavelength (253.7±1)nm. The UV illuminance meter can be used in the fields of medical treatment, epidemic prevention, optoelectronics, scalding, electric light source, chemical industry, building materials, meteorology, and aerospace.
The measuring instrument for measuring the intensity of ultraviolet radiation is called the receiving part of the ultraviolet radiation illuminance meter, which is generally composed of a receiving part, a releasing part and a display part. The receiving part consists of an electrical detector (usually a silicon photodiode), a band-pass glass filter or an interference light filter, and a diffuse transmission window. In this device, the detector (ultraviolet radiation probe) effectively converts the ultraviolet radiation it receives into an electrical signal, which is amplified by the electronic circuit and processed accordingly, and then displayed by an analog or digital meter. come out. From a practical point of view, the ultraviolet radiation received by the ultraviolet probe has a certain quantitative proportional relationship with the size of the electrical signal. Usually, the electrical signal under the radiation standard value is adjusted by electronic circuits to complete the calibration of the equipment. As far as the ultraviolet radiation meter is concerned, there are certain deviations in the structure of the instrument itself, the origin of the value and human factors, and the differences in the relevant standards and specifications, which eventually lead to the measurement results of the ultraviolet radiation meter. certain deviations occur.

Figure 1: The allowable error of XRP-3000 black and white light integrated illuminometer is ±5%
Note: The 3 black and white photometers in Figure 1 show that the value is within ±5%, indicating that the radiometer is qualified.
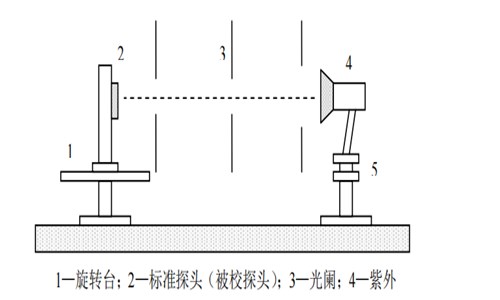
Figure 2: Radiometer Calibration Device
2. The main factors affecting the measurement results of the UV illuminance meter
Through the preliminary understanding of ultraviolet radiation and the discussion of the structure of the ultraviolet radiation meter, it can be known that there are many factors that affect the accuracy of the measurement results of the ultraviolet radiation meter.
2.1. UV light source affects UV light source in two aspects
First, because different UV illuminometers correspond to light sources of different wavelength bands, when the light source is not used properly, the measured values of the UV irradiance meter have huge differences. Therefore, it should be determined whether the actual light source and the UV irradiance meter match before use.
2.2. It is the influence of the instability of the UV light source. Especially for those newly purchased UV flaw detection lamps, there must be an aging process, and the stability of the UV light source will become better after aging. Therefore, before each use of the UV light source, the UV light source can be pre-ignited and preheated, generally for about 20 minutes, and the UV light source will gradually become stable. When using a black light high-pressure mercury lamp for measurement, firstly, in order to ensure the stability of the output ultraviolet irradiance of the black-light high-pressure mercury lamp, when in use, an AC voltage stabilized power supply can be used, and an AC voltage stabilizer can be used to achieve the stability of the input voltage.
(1) The influence of the verification device of the ultraviolet radiation illuminance meter. The UV radiation meter in use should be sent to the local metrology department for verification every year. In the process of measurement and verification, the accuracy of the verification device of the ultraviolet illuminance meter will affect the level judgment or error correction of the ultraviolet illuminance meter. The following factors affect the accuracy of the verification device of the ultraviolet radiation illuminance meter: the error caused by the traceability of the standard ultraviolet radiation illuminance measurement value, the error caused by the stability of the standard ultraviolet radiation illuminance meter, the optical platform used by the verification instrument due to the horizontal plane error The influence caused by the whole set of verification device, the error generated when the whole set of verification device is installed and debugged. From the above, the errors caused by the above unfavorable factors are attributed to systematic errors. After further analysis, it can be seen that the measurement uncertainty U of the UV illuminometers in different measurement bands during the verification is about 11.8%.
(2) The influence of the position of the UV illuminance meter during use. When measuring the irradiance of the UV illuminometer, the geometric center of the receiver and the optical center of the light source should be on the same axis, and the plane of the receiver and the optical axis of the light source must be at an angle of 90°. This contributes to the uncertainty of the UV light meter measurement results of about one percent.
(3) The influence of the unevenness of the irradiation surface of the ultraviolet light source. From a practical point of view, the most commonly used UV-A type ultraviolet light source produced in the United States, that is, the radiation surface of the black light high-pressure mercury lamp is circular; the UV-B type ultraviolet light source developed and produced by the China Institute of Metrology, namely The radiating surface of a low-pressure mercury lamp is rectangular. The non-uniformity of the irradiated surface of these UV light sources has a great influence on the actual measurement. At present, the optical axis is mainly used as the center, and the upper, lower, left and right distances from the optical axis are 20 mm. The measurement is carried out in this way, and the largest change is recorded. Practice has shown that the influence of the non-uniformity of the irradiated surface of the ultraviolet light source will have a huge impact on the measurement of the ultraviolet illuminance meter, so it should be improved in time.
(4) Influenced by the difference in cosine performance between the verified UV illuminance meter and the standard UV illuminance meter. From a practical point of view, there are certain differences in the cosine performance of UV radiation meters produced by different manufacturers, which will have a certain impact on the measurement results of UV radiation meters. Based on this, the author suggests that the light-emitting surface of the ultraviolet light source and the light-receiving surface of the receiver should be adjusted first, so that they are perpendicular to the optical axis as much as possible, and the center is located on the measured optical axis as much as possible, and then adjust the distance between the light source and the receiver. , and finally make this distance more than ten times larger than the light-emitting surface of the ultraviolet light source. At this time, adjust the diaphragm appropriately to ensure that it just does not block the light projected by the ultraviolet light source to the receiver; rotate the receiver left and right, measure 0 degrees, 1 to 10 degrees, and 10 degrees to -1 degrees respectively, and use 1 degree is the standard interval, measure its value, and then calculate the theoretical values of the above points through the cosine law, and calculate their errors on this basis.